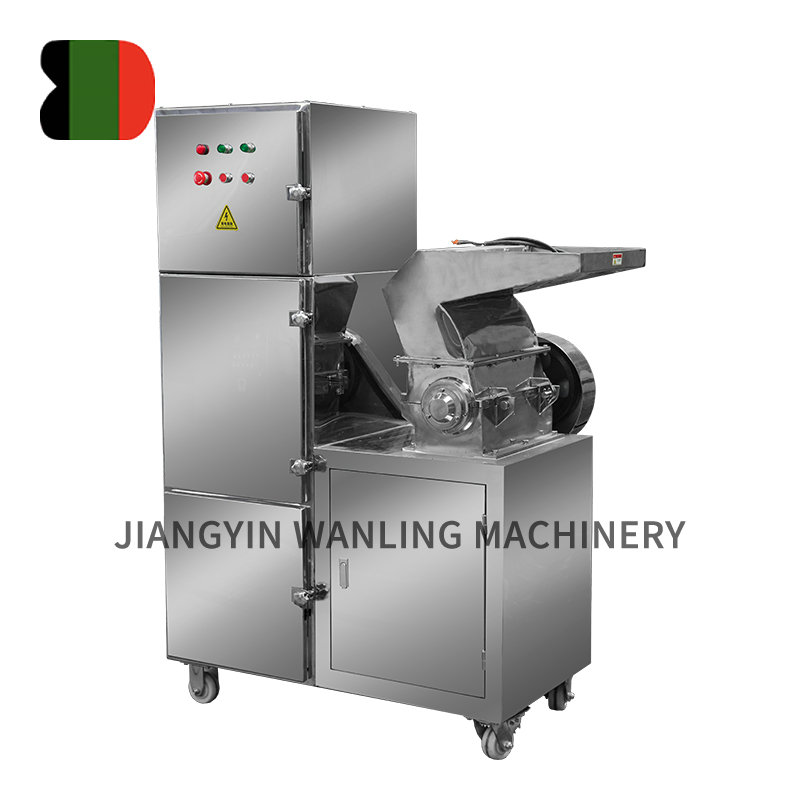
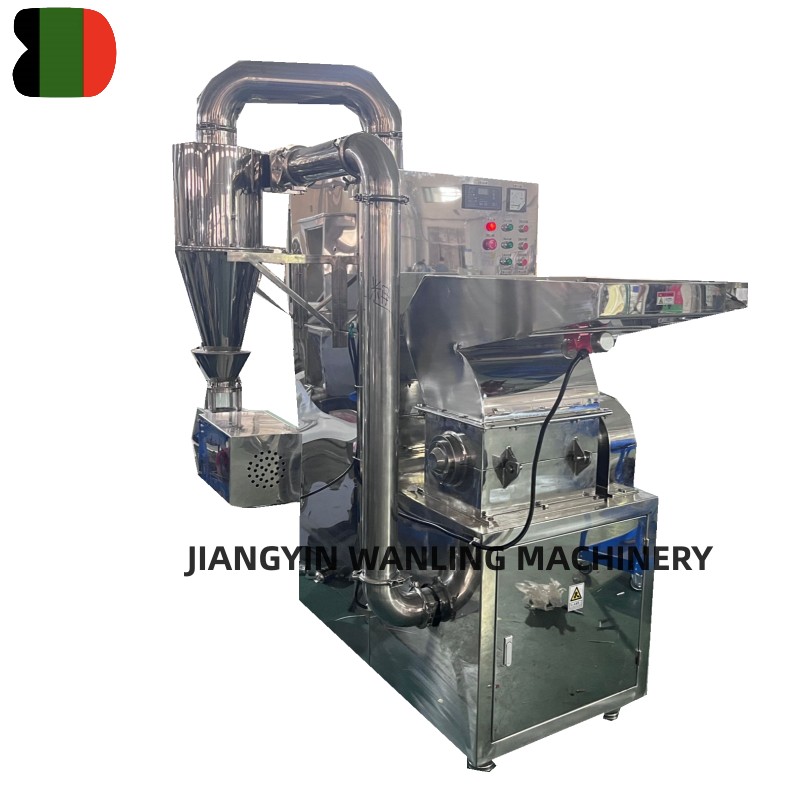
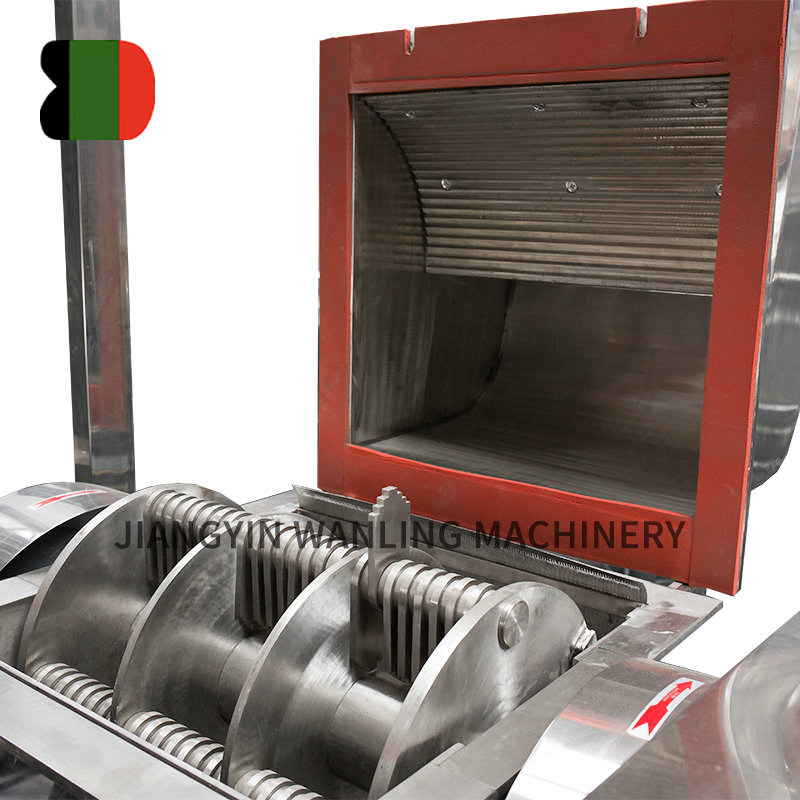
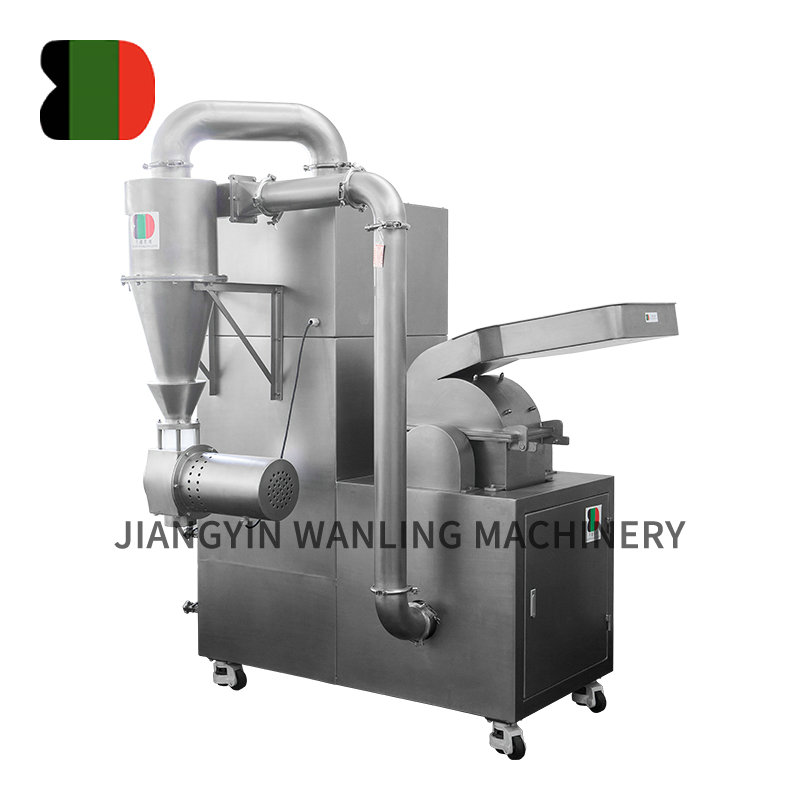
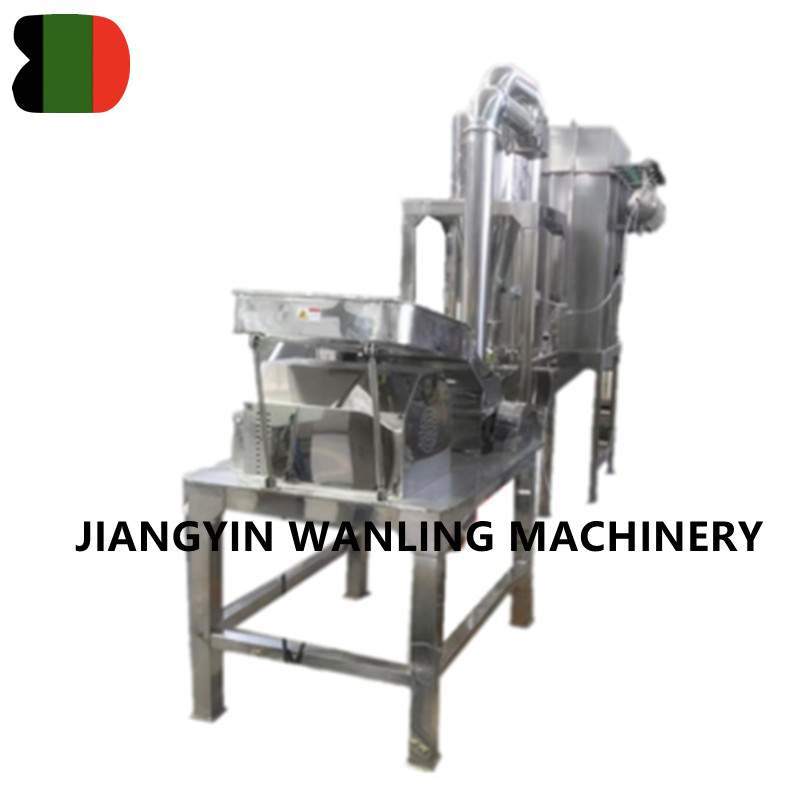
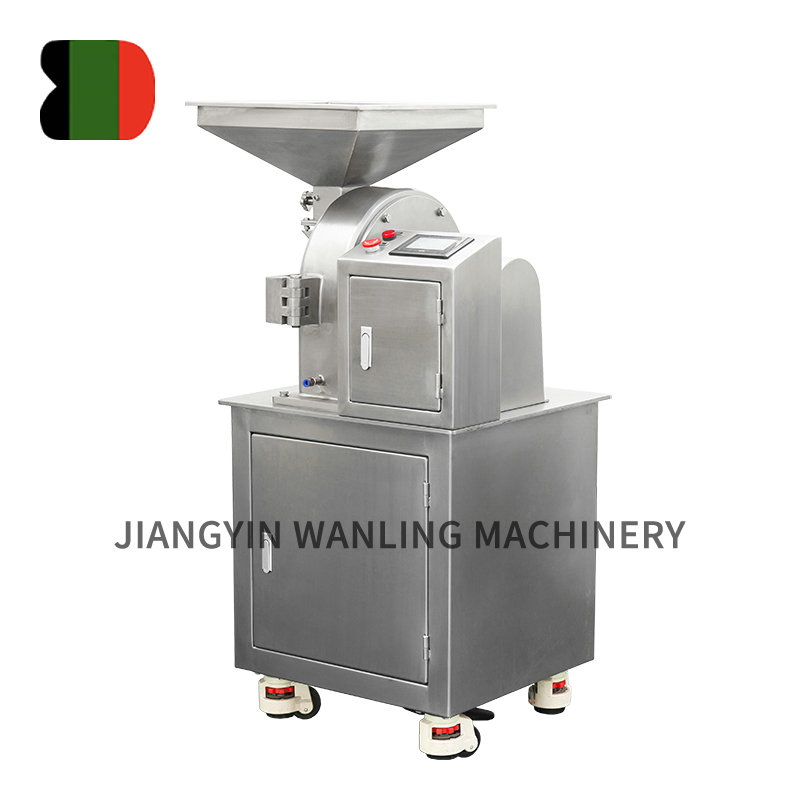
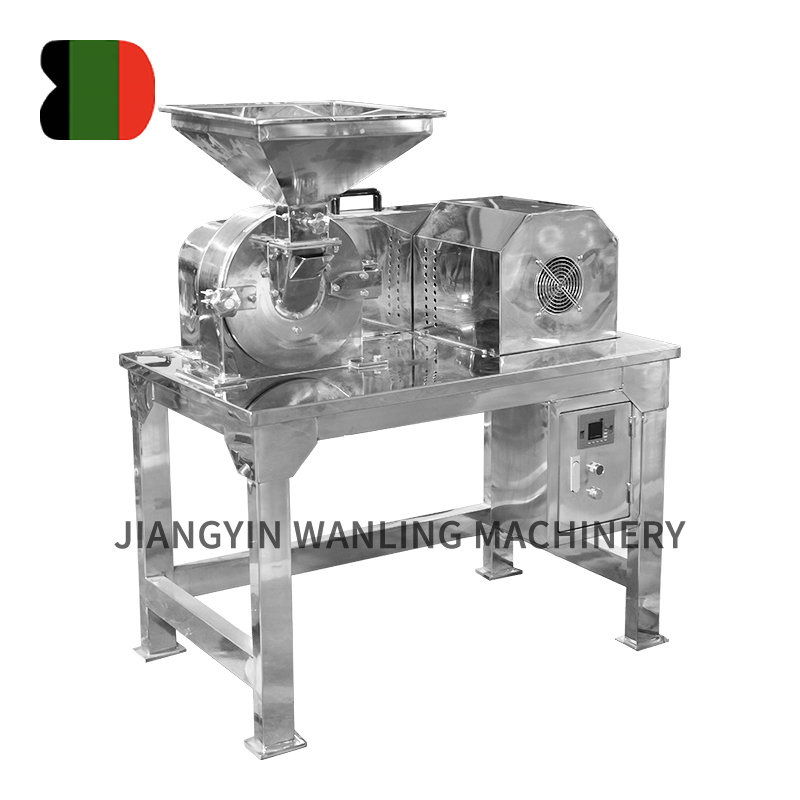
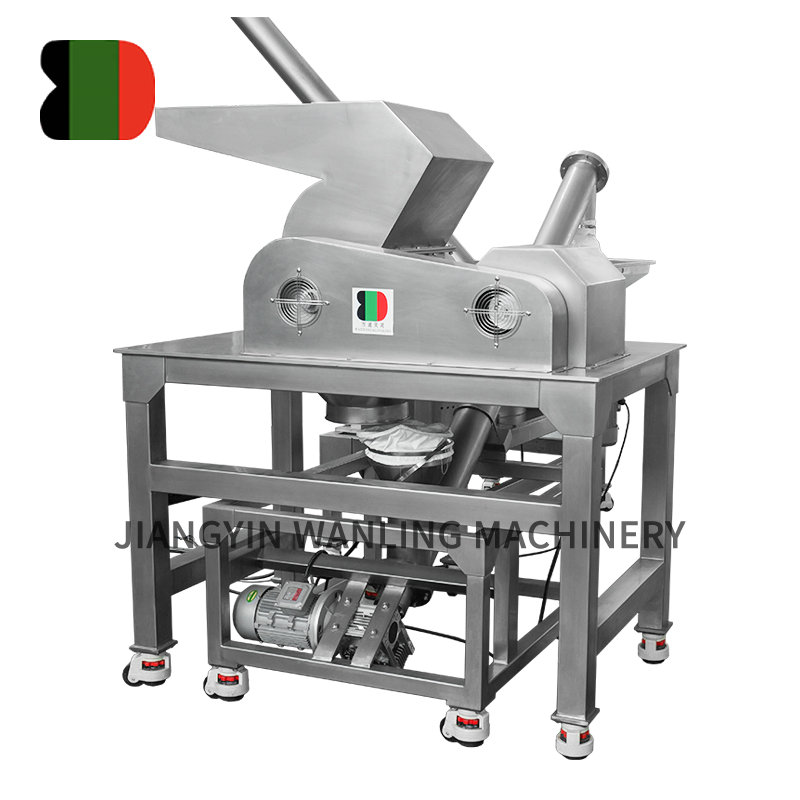
Ensuring hygienic handling during vacuum conveyor transportation is critical, especially in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals. Here are key measures typically taken to maintain hygiene:
Material and Construction:
Food-Grade Materials: Use of food-grade or pharmaceutical-grade materials for all contact surfaces to prevent contamination.
Smooth Surfaces: Smooth, non-porous surfaces are used to prevent material buildup and facilitate easy cleaning.
Design Features:
Sealed System: Vacuum conveyors are designed to be fully enclosed to minimize exposure to contaminants and ensure that materials are transported in a controlled environment.
Sanitary Design: Designs that minimize crevices and joints where material can accumulate and become a source of contamination.
Cleaning Protocols:
Easy Disassembly: Components that come into contact with materials should be easy to disassemble for thorough cleaning and sanitizing.
Washdown Capabilities: Systems should be capable of withstanding washdown procedures, including the use of high-pressure water and cleaning agents.
Air Filtration:
HEPA Filters: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are often used to capture airborne contaminants and prevent them from entering the system or escaping into the environment.
Cyclone Separators: These can be used to remove larger particles and prevent them from reaching sensitive parts of the conveyor system.
Ensuring hygienic handling during vacuum conveyor transportation is critical, especially in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals. Here are key measures typically taken to maintain hygiene:
Material and Construction:
Food-Grade Materials: Use of food-grade or pharmaceutical-grade materials for all contact surfaces to prevent contamination.
Smooth Surfaces: Smooth, non-porous surfaces are used to prevent material buildup and facilitate easy cleaning.
Design Features:
Sealed System: Vacuum conveyors are designed to be fully enclosed to minimize exposure to contaminants and ensure that materials are transported in a controlled environment.
Sanitary Design: Designs that minimize crevices and joints where material can accumulate and become a source of contamination.
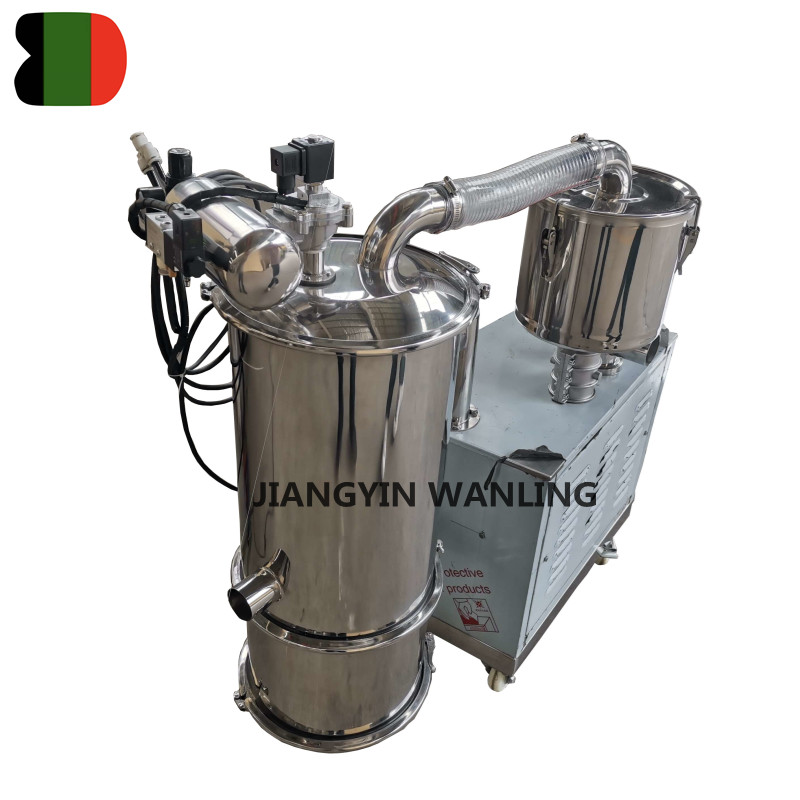

Cleaning Protocols:
Easy Disassembly: Components that come into contact with materials should be easy to disassemble for thorough cleaning and sanitizing.
Washdown Capabilities: Systems should be capable of withstanding washdown procedures, including the use of high-pressure water and cleaning agents.
Air Filtration:
HEPA Filters: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are often used to capture airborne contaminants and prevent them from entering the system or escaping into the environment.
Cyclone Separators: These can be used to remove larger particles and prevent them from reaching sensitive parts of the conveyor system.
Regular Maintenance:
Scheduled Inspections: Regular inspections and maintenance schedules to identify and address any potential sources of contamination or wear.
Cleaning Logs: Keeping detailed logs of cleaning procedures and maintenance activities to ensure compliance with hygiene standards.
Control Systems:
Contamination Detection: Advanced systems may include sensors to detect contamination or blockages and alert operators to potential hygiene issues.
Automated Cleaning: Some systems feature automated cleaning cycles to ensure thorough and consistent hygiene practices.
Operator Training:
Hygiene Training: Providing operators with training on proper hygiene practices, including handling procedures and cleaning protocols.
Safety Procedures: Training on safety procedures to prevent contamination during operation and maintenance.
Compliance with Standards:
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring the system complies with relevant industry standards and regulations, such as FDA or GMP guidelines for food and pharmaceutical applications.
Implementing these measures helps maintain high standards of hygiene and ensures that the vacuum conveyor system operates efficiently while safeguarding the quality of the transported materials.
Regular Maintenance:
Scheduled Inspections: Regular inspections and maintenance schedules to identify and address any potential sources of contamination or wear.
Cleaning Logs: Keeping detailed logs of cleaning procedures and maintenance activities to ensure compliance with hygiene standards.
Control Systems:
Contamination Detection: Advanced systems may include sensors to detect contamination or blockages and alert operators to potential hygiene issues.
Automated Cleaning: Some systems feature automated cleaning cycles to ensure thorough and consistent hygiene practices.
Operator Training:
Hygiene Training: Providing operators with training on proper hygiene practices, including handling procedures and cleaning protocols.
Safety Procedures: Training on safety procedures to prevent contamination during operation and maintenance.
Compliance with Standards:
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring the system complies with relevant industry standards and regulations, such as FDA or GMP guidelines for food and pharmaceutical applications.
Implementing these measures helps maintain high standards of hygiene and ensures that the vacuum conveyor system operates efficiently while safeguarding the quality of the transported materials.


 Español
Español