Coating Machine Manufacturer
-
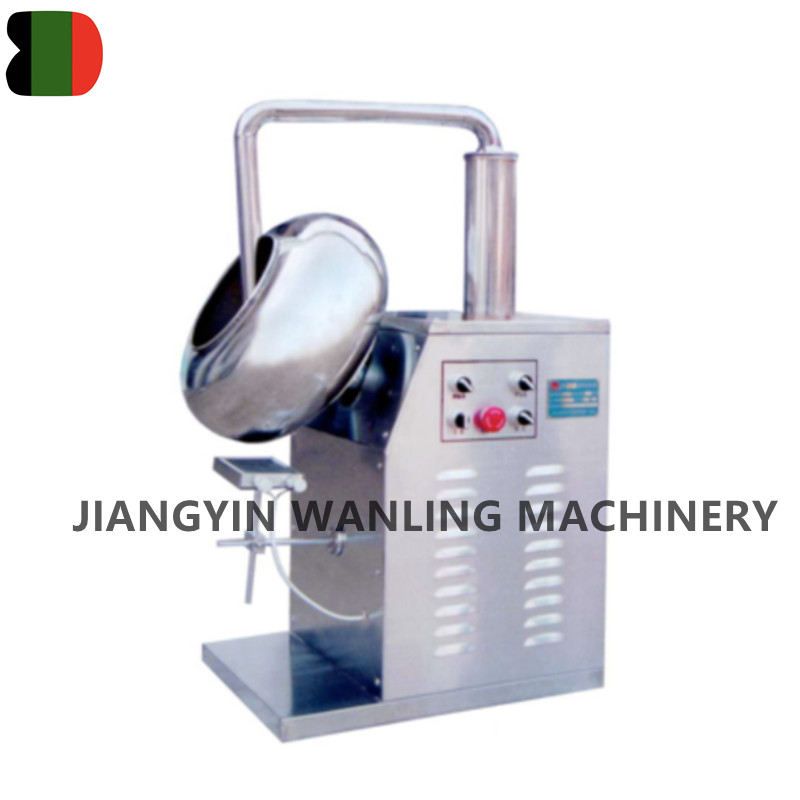


BTJ Chocolate Coating Processing Machine
It is specially used to sugar coating pills and tablets in the lines of pharmacy,foodstuff and chemicals,as well as for the roll-making,and ... -
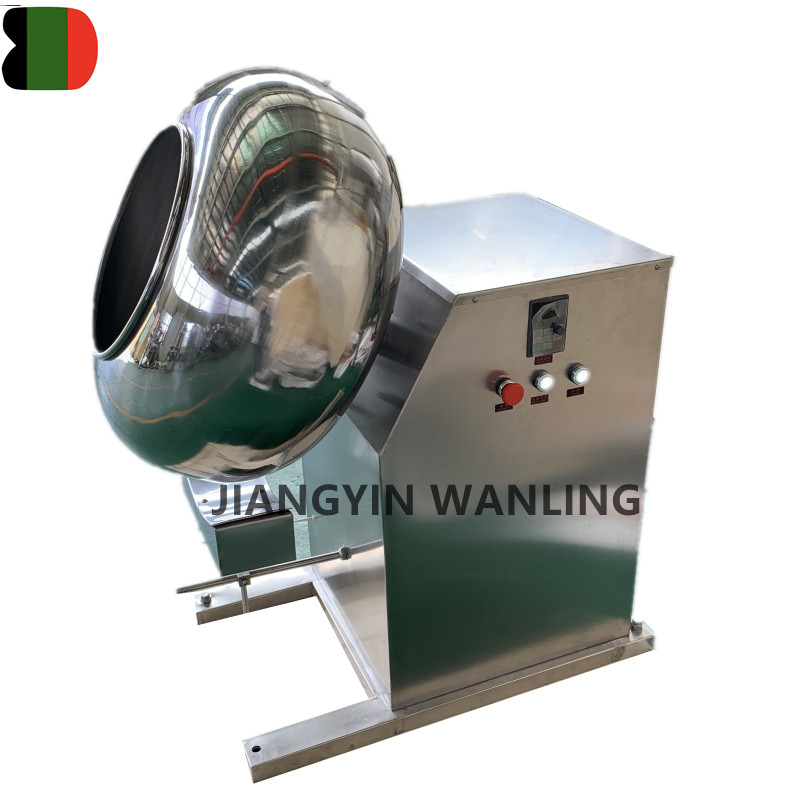


BTJ Stainless Steel Peanut Almond Nuts Sugar Candy Coating Pan Machine
It is specially used to sugar coating pills and tablets in the lines of pharmacy,foodstuff and chemicals,as well as for the roll-making,and ... -


BTJ multi-function nuts coating machine
The nuts coating machine is specially used to coating pills and tablets in the lines of pharmacy,foodstuff and chemicals,as well as for the ...
This coating machine is mainly used in pharmaceutical industry pills, sugar-coated tablets production, it can also be used in food, light industry, chemical industry, spherical or granular material, mixing and lighting. For example: chocolate polishing, coat peanuts, sugar, spices, rice balls manufacturing etc.
The machine is mainly used in the pharmaceutical industry in the pill, tablets of sugar coating production, can also be used for food, light industry, chemical industry in the spherical or granular materials, rolling, mixing and lighting.

About Us
Honor
-
 Honor
Honor -
 CE
CE
News
-
Industry News 2025-12-23
Introduction to Double Cone Blenders Double cone blenders are widely used industrial mixing machines...
View More -
Industry News 2025-12-18
Introduction to Spice Grinding Machines Spice grinding machines are essential tools for both commerc...
View More -
Industry News 2025-12-12
How to Choose the Right Ribbon Blender for Powder and Granule Mixing Choosing a ribbon blender for ...
View More -
Industry News 2025-12-07
Introduction: The Versatile Workhorse of Size Reduction In the vast landscape of industrial processi...
View More
Industry Knowledge Expansion
Are there some tips to save coating machine time and resources?
Here are some tips to save time and resources when using coating machines:
Optimize Process Parameters: Fine-tune the coating machine parameters such as coating speed, temperature, and pressure to achieve the desired coating results while minimizing wastage of materials and energy.
Routine Maintenance: Implement a regular maintenance schedule for the coating machine to ensure optimal performance and prevent unexpected downtime. This includes cleaning, lubricating, and inspecting components for wear and tear.
Preventive Maintenance: Proactively address potential issues before they escalate by conducting preventive maintenance tasks such as replacing worn-out parts, calibrating equipment, and checking for leaks or blockages.
Training and Education: Provide comprehensive training to machine operators on proper operating procedures, troubleshooting techniques, and maintenance practices. Well-trained operators can identify and resolve issues quickly, reducing downtime and material waste.
Material Management: Efficiently manage coating materials by accurately measuring and monitoring consumption, minimizing spills and overuse. Implement inventory management systems to track material usage and reorder supplies in a timely manner to avoid delays.
Quality Control: Implement robust quality control measures to ensure consistent coating quality and minimize rework. Perform regular inspections and tests to identify defects early in the process, preventing wastage of materials and time.
Streamline Workflow: Analyze and streamline the coating process workflow to minimize idle time and maximize machine utilization. Optimize material flow, layout, and sequencing to eliminate bottlenecks and reduce waiting times.
Invest in Automation: Consider investing in automation technologies such as robotic coating systems or programmable controls to improve efficiency, accuracy, and repeatability of the coating process. Automation can reduce manual labor requirements and increase throughput.
Energy Efficiency: Implement energy-saving measures such as using energy-efficient equipment, optimizing heating and cooling systems, and minimizing idle machine time. Consider renewable energy sources or energy recovery systems to reduce energy consumption and costs.
Continuous Improvement: Foster a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging feedback from operators, monitoring key performance indicators, and implementing process improvements based on data analysis. Regularly review and update procedures to incorporate best practices and innovations.
How to evaluate the quality of the coating produced by the coating machine?
Evaluating the quality of the coating produced by a coating machine is crucial to ensure that it meets the desired standards and specifications. Here are some methods commonly used to evaluate coating quality:
Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the coated surface to assess its appearance, uniformity, and smoothness. Look for defects such as streaks, bubbles, pinholes, or uneven coverage that may indicate problems with the coating process.
Thickness Measurement: Use thickness measurement tools such as micrometers, calipers, or coating thickness gauges to measure the thickness of the coating layer. Compare the measured thickness to the target thickness specified in the coating requirements to ensure compliance.
Adhesion Testing: Perform adhesion tests to evaluate the bond strength between the coating and the substrate. Methods such as cross-cut or pull-off adhesion tests can assess the adhesion quality by determining the resistance of the coating to detachment or peeling.
Surface Roughness Measurement: Measure the surface roughness of the coated surface using profilometers or surface roughness testers. Evaluate whether the surface roughness meets the specified requirements, as excessive roughness may affect the performance or aesthetics of the coating.
Gloss Measurement: Use gloss meters to measure the gloss or shine of the coated surface. Compare the measured gloss values to the target gloss levels specified in the coating requirements to ensure consistency and uniformity.
Color Measurement: Use colorimeters or spectrophotometers to measure the color of the coated surface. Compare the measured color values to the target color standards to ensure color accuracy and consistency across batches.
Durability Testing: Subject the coated surface to durability tests such as abrasion resistance, scratch resistance, chemical resistance, or corrosion resistance tests. Evaluate the performance of the coating under simulated or real-world conditions to assess its long-term durability and reliability.
Film Integrity Testing: Conduct film integrity tests to check for defects such as cracks, delamination, blistering, or peeling in the coating film. Methods such as tape tests or solvent rub tests can assess the integrity and robustness of the coating layer.
Microscopic Examination: Use microscopy techniques such as optical microscopy or electron microscopy to examine the coating structure and morphology at a microscopic level. Identify any defects, contaminants, or irregularities that may affect coating quality.
Customer Feedback: Seek feedback from end-users or customers regarding their satisfaction with the coated products. Consider factors such as appearance, performance, durability, and reliability to assess overall customer satisfaction with the coating quality.
By employing these evaluation methods, manufacturers can thoroughly assess the quality of the coating produced by the coating machine and identify any areas for improvement to ensure consistent and reliable coating performance.


 Español
Español