Mixer Machine Manufacturer
-


WLV V Shaped Food Powder Mixer Machine
This v mixer machine is applicable to mix dry powder and granule material for the pharmacy and other relative industries. -

WLV Stainless Steel V Cone Mixer Machine
The stainless steel v cone mixer have many models,the smalles one is WLV-200 mixer,its capacity is 40kg per batch,that means the mixer can m... -

WLW Double Cone Type Powder Blender Machine
This WLW double cone mixer machine has the advantages of simple operation, uniform mixing, feeding can be equipped with vacuum suction devic... -

WLW Double Cone Powder Drum Mixer Machine
The double cone mixer features: Simple operation and uniform mixing: The tumbling motion within the double cones gently folds and mixes the ... -


WLS High Quality Medicine Powder 3d Mixer
The 3d swing mixer machine is widely used for the mixing of powder materials in the industry of pharmacy, chemical industry, food and so on;... -

WLS Pharmaceutical Powder 3d Drum Mixer Mixing Machine
Applications: Mixing powder materials in various industries including pharmaceutical, chemical, and food. Effective for blending materials w... -


WLLD Horizontal Type Spice Mixing Ribbon Mixer Machine
The ribbon mixer machine is full stainless steel mixer, horizontal ribbon mixer shaft is arranged on the transmission screw blade, the inter... -


WLLD High Quality Food Powder Ribbon Mixer Blender Machine
MACHINE DESCRIPTION Installed on the stirring shaft of the spiral drive inside and outside diameter of the material in the cylinder, the agi... -


CH Single Paddle Flour Tank Mixer Machine
CH series groove mixer, mainly composed by the cell body and agitator, bracket, flip part, transmission part and electrical components. -

SCH Double Paddle Food Powder Mixer
SCH series groove mixer, mainly composed by the cell body and agitator, bracket, flip part, transmission part and electrical components. -

SHJ Vertical Type Double Screw Mixer
This vertical double screw mixer machine is a new type of high efficiency & high precision mixing equipment, widely used in pharmaceutic... -

SHJ High Speed Rotary Double Screw Conical Mixer
SHJ high speed rotary double screw conical mixer is a type of industrial machine used for efficiently and precisely blending dry powders.It ... -


EYH horizontal type fertilizer 2d moving mixer
The drum of 2D mixer machine can simultaneously move in two directions, one for the rotation of the drum, another for drum with the swinging... -


EYH Horizontal Two Dimensional 2d Movement Drum Mixer Blender
Traditional drum mixers rely solely on rotation to achieve material blending. While this method works, it can be slow and may not guarantee ... -


FZ Stainless Steel Powder Bin Cone Mixer
FZ series square cone shape blender is widely applied in the industry of pharmaceutics, chemicals, metallurgy, food and feedstuff. It is a n...
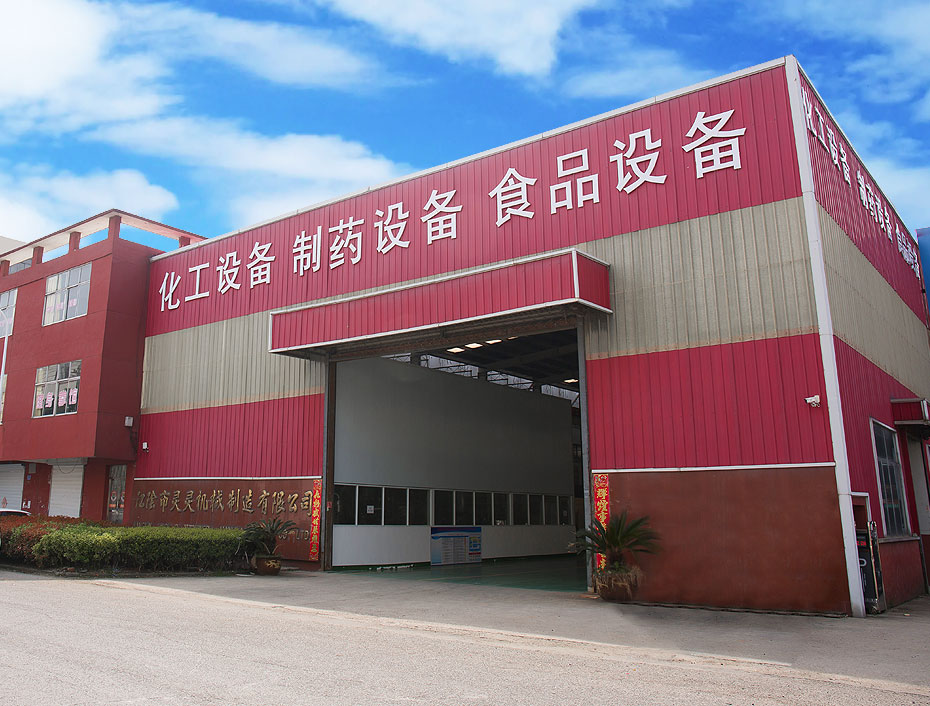

About Us
Honor
-
 Honor
Honor -
 CE
CE
News
-
Industry News 2025-01-17
The grinding mechanisms in powder grinding machines significantly influence the size and uniformity ...
View More -
Industry News 2025-01-10
Minimizing the risk of cross-contamination when cleaning double cone blenders is critical, especiall...
View More -
Industry News 2025-01-03
1. Air-to-Air Heat ExchangerHow It Works: An air-to-air heat exchanger transfers heat from the warm ...
View More -
Industry News 2024-12-23
1. Impact of Material Shape on GranulationIrregular-Shaped MaterialsCharacteristics: Irregular mater...
View More
Industry Knowledge Expansion
What factors are related to the amount of liquid discharged by the mixer machines?
The discharge capacity of a mixer’s blades is closely related to several key factors:
Flow number of the blades themselves: The design of the blades directly affects their flow number, which is one of the crucial factors determining the discharge capacity of the blades.
Blade rotation speed: The rotation speed of the blades is an important factor affecting the discharge capacity. Given a fixed blade diameter, a higher rotation speed generally results in a greater discharge capacity. However, it should be noted that excessively high rotation speeds can lead to increased energy consumption and potential damage to the mixer.
Blade diameter: The discharge capacity is proportional to the cube of the blade diameter. This means that, under the same conditions, using blades with a larger diameter can achieve a greater discharge capacity.
Mixer design: The overall design of the mixer also impacts the discharge capacity. Factors such as the number of mixers, the specifications of the discharge outlet, and its position can all influence the discharge capacity. Therefore, when selecting a mixer machine, an appropriate design should be chosen based on specific conditions.
The discharge capacity of a mixer’s blades is mainly influenced by the flow number of the blades themselves, the blade rotation speed, the blade diameter, and the mixer design. In practical applications, adjusting these parameters can optimize the performance of the mixer to meet different mixing needs.
How do different blade designs in mixer machines affect the mixing of viscous versus granular materials?
Blade designs in mixers are tailored to the properties of the materials being processed. For viscous materials, such as dough or thick pastes, blades with a high shear rate and a wide surface area are preferred. These blades facilitate the breakup of large aggregates and promote uniform distribution of ingredients throughout the mixture. Moreover, the blade's shape and orientation can influence the flow pattern within the mixing chamber, ensuring efficient mixing without causing excessive strain on the motor.
In contrast, when dealing with granular materials like powders or grains, the mixing dynamics are different. Blades with a gentler action are typically employed to prevent excessive breakage or degradation of the particles. Additionally, these blades may incorporate features such as scoops or baffles to enhance particle movement and prevent clumping. By optimizing the blade design for granular materials, mixers can achieve thorough blending while preserving the integrity of the individual particles.
The selection of blade design is critical in achieving optimal mixing performance for both viscous and granular materials. By understanding the unique rheological properties and mixing requirements of each material type, manufacturers can design mixers that deliver consistent results across a wide range of applications.


 Español
Español